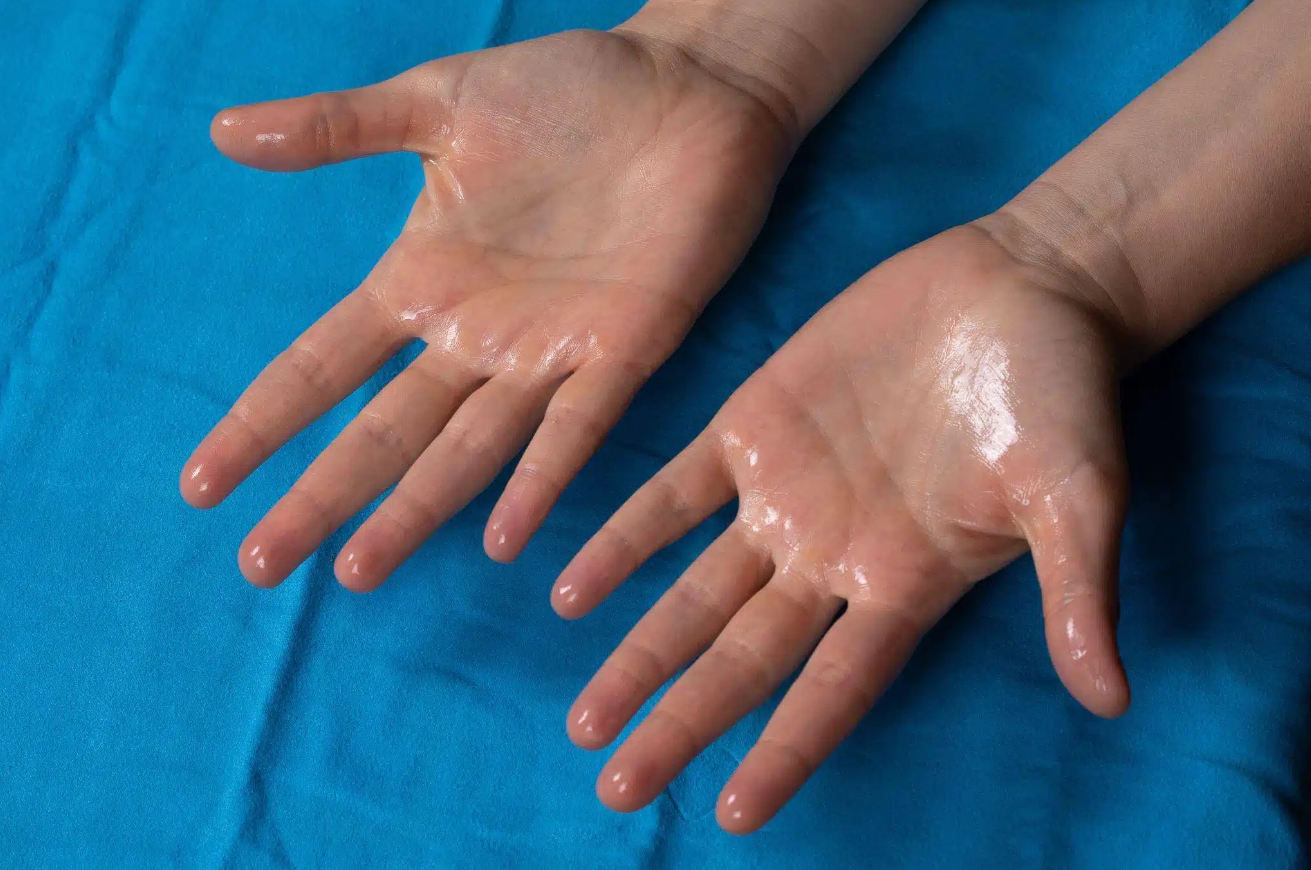
Excessive Sweating
Hyperhidrosis (Excessive Sweating) Treatment
What Is Hyperhidrosis?
Excessive sweating, compensatory sweating, or hyperhidrosis, is a condition wherein a person sweats more than is necessary to regulate normal body temperature. It can affect the whole body or regions like the hands (sweaty palms or palmar hyperhidrosis), feet, underarms, or face. It is either primary hyperhidrosis, with no apparent medical cause, or secondary hyperhidrosis, which occurs with medical conditions or medications. The sweating can occur even in cold climates or without physical activity. This condition can interfere with daily life, causing embarrassment, body odour and discomfort. Some medical and skin conditions associated with excessive sweating or overgrowth of bacteria (eg, obesity, diabetes mellitus, fungal infections) can cause unpleasant body odor.
What causes hyperhidrosis / excessive sweating?
Sweating is a natural way for the body to cool down. However, in some cases, the sweat glands do not stop sweating even if there's no reason for them to. This is called hyperhidrosis. Initial evaluations include a thorough medical history and assessment to identify underlying causes and the extent of the condition.
Hyperhidrosis can be caused by different factors. It can be inherited, or you can get it from some health conditions like diabetes, thyroid problems, anxiety disorders, or menopause.
Types Of Hyperhidrosis
Primary Hyperhidrosis (Focal Hyperhidrosis)
Cause: Unknown medical cause (idiopathic).
Patterns:
Impacts specific locations (focal), such as palms, soles, underarms, or face.
Symmetrical — both sides of the body are usually affected equally.
Onset: Usually begins in childhood or adolescence.
Triggers: Stress, heat, or no trigger at all.
Occurs during sleep? Usually doesn't occur while asleep.
Family history: Usually hereditary — runs in families.
Secondary hyperhidrosis (Generalized Hyperhidrosis)
Cause: medical history, underlying medical conditions or side effect of mediactions (e.g., diabetes, infection, hyperthyroidism, menopause, some medications).
Patterns:
Involves larger portions or the entire body (generalized).
Not necessarily symmetrical.
Onset: Can begin at any age, depending upon when the underlying issue occurs.
Triggers: Usually related to the underlying cause.
Occurs during the night? May occur during the night (night sweats).
Family history: Infrequently hereditary.
Hyperhidrosis Treatment Options in Singapore
If there is an underlying cause to hyperhidrosis (sweaty palms / feets), the contributing health condition will be treated first. But for hyperactive sweat glands, the following treatment options are chosen focusing on controlling how much a person sweats.
Botulinum Toxins is an effective treatment for localized hyperhidrosis. These injections block the nerves that trigger the nerve signals responsible for sweating in affected areas, stopping the sweat glands from producing too much sweat, may be considered for localized hyperhidrosis when other treatments have failed.
How it works: Temporarily blocks nerves that trigger sweat glands.
✅ Pros: Highly effective for localized sweating (e.g., underarms).
❌ Cons: Expensive; effects last 4–6 months.
Oral Medications (Anticholinergics) block acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that assists in stimulating sweat glands. Blocking this signal makes the body release less sweat.
How it works: Reduces overall sweat production.
✅ Pros: Useful for generalized sweating.
❌ Cons: Side effects like dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation.
Antiperspirant products of clinical strength contain higher concentration of aluminum chloride (usually 10–20%) than do regular over-the-counter deodorants. They operate by temporarily closing off the sweat ducts, reducing the amount of sweat that reaches the skin's surface.
How it works: Blocks sweat glands using aluminum chloride.
✅ Pros: Easy to use, affordable, non-invasive.
❌ Cons: Can cause skin irritation; less effective for severe cases
What Cause Body Odour?
Body odor may result from dried sweat on clothing, as well as from certain medical conditions, foods, or medications. It is often worsened by excessive sweating or poor personal hygiene. Certain medical conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, and fungal infections—that are linked to excessive sweating or bacterial overgrowth—may also lead to bad body odor. The condition can be treated by good personal hygiene and using antiperspirants. For worse cases, botulinum toxin (Botox) injections work by reducing sweat production, hence reducing skin moisture and bacterial activity, and consequently eliminating the associated odour.
Is there a permanent cure for hyperhidrosis?
Some people with hyperhidrosis are lucky and their condition goes away on its own. But for most people with excessive sweating, it is not likely that the problem will go away without treatment.
There are different treatments available, but they vary in their permanence. Botulinum Toxin usually needs to be done again every 6 months for control sweating, while more permanent like Sympathectomies usually require a Neurosurgery consult.

FAQs
-
Yes, Botox injections are very safe when performed by trained and experienced professionals.
-
Besides some bruising and soreness, no downtime is expected.
-
Normally 1 session with a review is required.
-
Usually within 1-2 weeks.
-
For best results, we recommend top up sessions every 4-6 months.